How Continuous Validation Improves Stability, Performance, and Compatibility
As enterprise IT environments become more complex, traditional “test-before-deploy” validation models are no longer sufficient. Modern server infrastructures are dynamic—firmware updates, OS patches, driver changes, and workload shifts happen continuously. In this environment, real-time testing and monitoring tools have become essential to ensure stability, performance, and long-term compatibility.
Rather than replacing structured compatibility checklists, real-time monitoring tools extend validation into production, creating a continuous feedback loop that significantly reduces operational risk. This article explores how real-time tools automate validation, reviews widely adopted solutions in the market, and explains how they complement a pre-validated configuration checklist for enterprise-grade reliability.
Why Real-Time Validation Matters in Modern Server Environments
Traditional compatibility testing answers one question:
“Does this configuration work today?”
Real-time testing and monitoring answer a far more critical one:
“Is this configuration still working as expected under real workloads?”
Enterprise failures rarely occur at boot time. They emerge gradually—under thermal stress, I/O saturation, firmware edge cases, or unexpected workload combinations. Without real-time visibility, these issues often go unnoticed until they escalate into outages.
Real-time validation enables organizations to:
Detect early warning signals before failures occur
Correlate performance anomalies with specific hardware or firmware layers
Validate configuration assumptions under actual production conditions
Reduce mean time to diagnosis (MTTD) and recovery (MTTR)
Core Capabilities of Real-Time Server Validation Tools
Effective real-time testing and monitoring platforms share several critical capabilities:
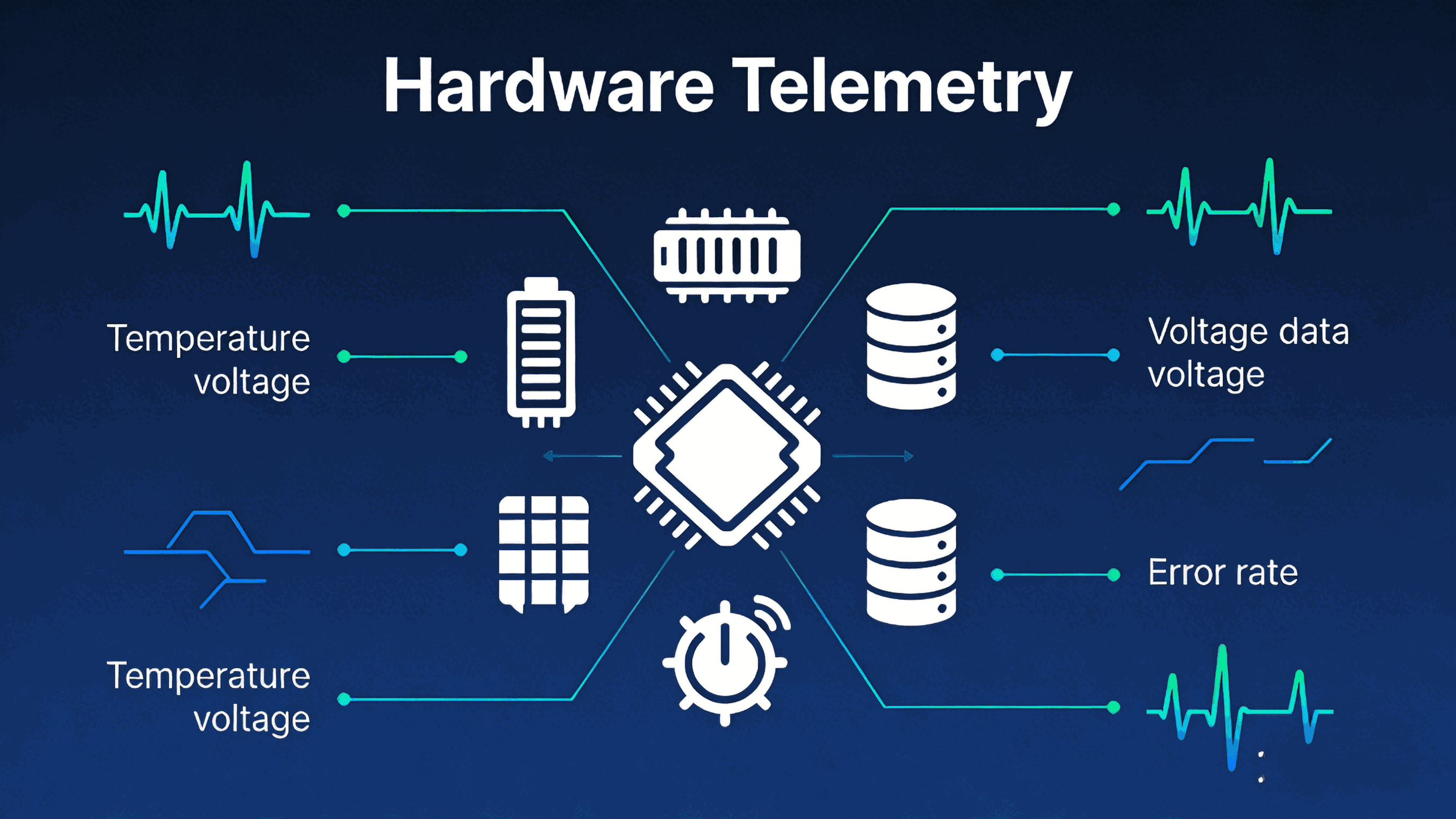
1. Hardware Health and Telemetry Monitoring
These tools continuously track:
CPU temperature and throttling behavior
Memory error rates (ECC, correctable vs. uncorrectable)
Power consumption and voltage stability
Storage wear, latency, and error patterns
This data reveals whether a configuration is operating within validated tolerances—or drifting toward failure.
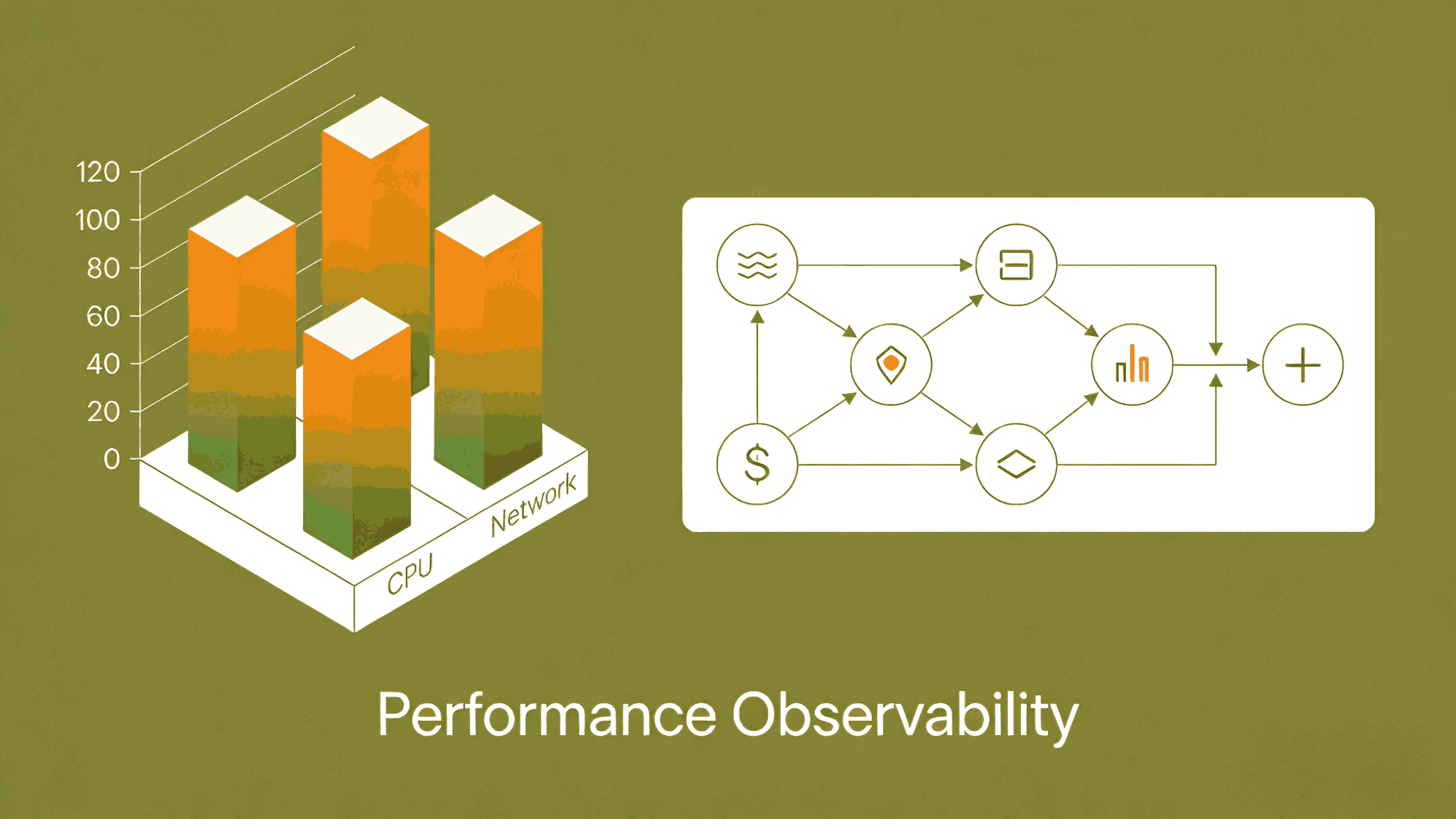
2. Performance and Workload Observability
Real-time observability platforms analyze:
CPU, memory, storage, and network utilization
Latency spikes under peak load
NUMA imbalance and PCIe bottlenecks
IO queue depth and throughput anomalies
This ensures that a configuration is not just “compatible,” but efficient and predictable.
3. Firmware, Driver, and OS Compatibility Detection
Modern tools can flag:
Firmware-driver mismatches
Unsupported kernel or hypervisor combinations
Regression risks after updates
Inconsistent versions across server fleets
This is especially critical in environments where partial updates introduce hidden incompatibilities.
Popular Real-Time Testing and Monitoring Tools in the Market
While enterprises often combine multiple tools, several categories dominate real-time validation:
Hardware-Level Monitoring Platforms
Vendor and industry-standard solutions provide low-level telemetry from CPUs, memory, storage, and power subsystems. These tools excel at detecting physical instability and hardware degradation.
Infrastructure and Performance Monitoring Tools
Widely adopted observability platforms aggregate metrics across servers, virtual machines, and workloads. They provide trend analysis, anomaly detection, and alerting, helping teams spot performance regressions early.
Log and Event Correlation Systems
By correlating firmware logs, OS events, and application errors, these tools help identify root causes across the stack, rather than treating symptoms in isolation.
While each tool category has strengths, no single platform guarantees compatibility on its own—which is why structured validation frameworks remain essential.
How Real-Time Tools Complement a Pre-Validated Configuration Checklist
A Pre-Validated Configuration Checklist defines the known-good baseline:
Approved hardware SKUs
Tested firmware and BIOS versions
Supported OS and driver combinations
Verified thermal and power envelopes
Real-time tools do not replace this baseline—they enforce it.
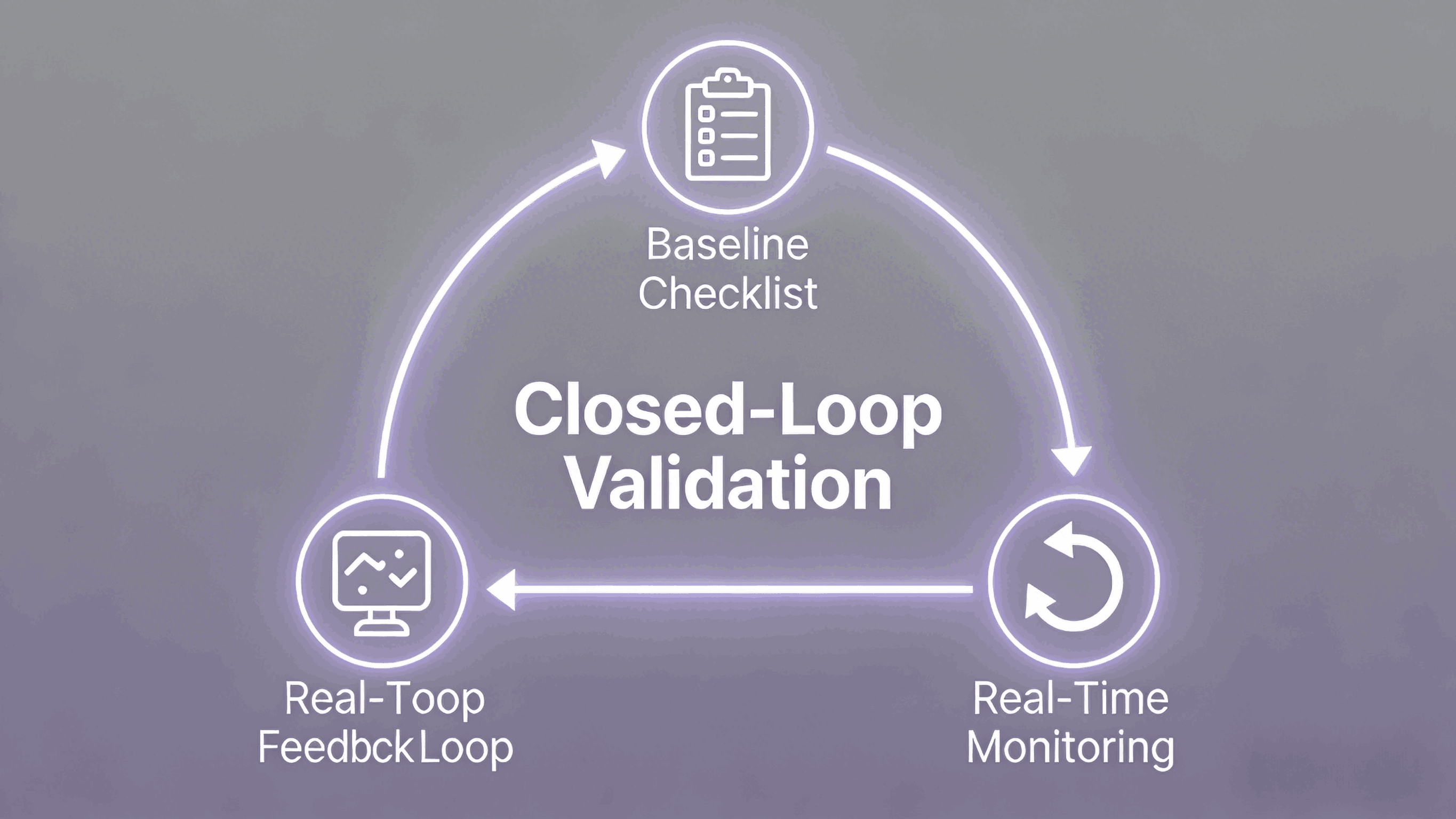
Together, they form a closed-loop validation system:
Checklist establishes the baselinePrevents unsupported or risky configurations from entering production.
Real-time monitoring enforces complianceDetects drift caused by updates, replacements, or workload changes.
Feedback improves future validationReal-world telemetry feeds back into the checklist, strengthening future testing.
This approach transforms compatibility testing from a one-time gate into a living system.
Operational and Business Benefits
Organizations that combine structured validation with real-time monitoring consistently achieve:
Fewer production incidents
Lower unplanned downtime
Faster root-cause analysis
More predictable performance
Reduced operational and support costs
From an executive perspective, this translates directly into lower risk, higher service reliability, and better ROI on infrastructure investments.
Conclusion: Continuous Validation Is the New Standard
In modern data centers, compatibility is no longer a static checkbox—it is a continuous state.
Real-time testing and monitoring tools extend validation beyond the lab, ensuring that server configurations remain stable, performant, and compatible throughout their lifecycle. When combined with a Pre-Validated Configuration Checklist, they create a resilient, scalable framework for enterprise IT operations.
As infrastructure complexity continues to grow, organizations that adopt continuous validation will outperform those relying on periodic testing alone.




